Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is one of the most common nerve-related conditions affecting the hand and wrist. Often seen in people who perform repetitive hand movements, especially involving typing, sewing, or working with tools, CTS can interfere with daily activities and significantly affect quality of life. In this blog post, we will dive deep into Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and how to prevent it.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
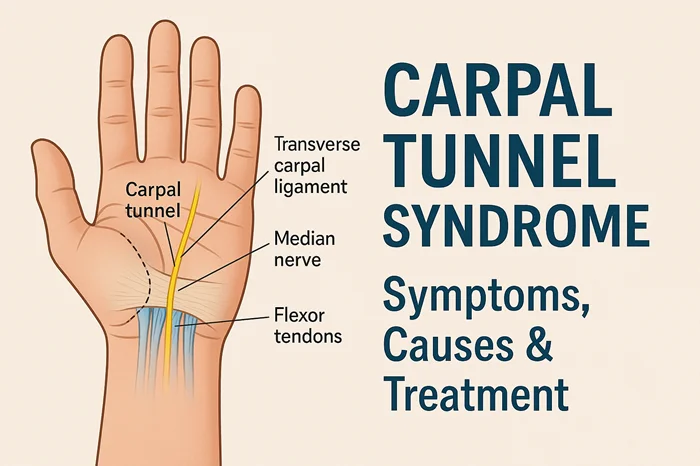
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway of ligament and bones at the base of the hand that houses the median nerve and tendons. When the tissues surrounding the tendons swell or thicken, they reduce the space in the carpal tunnel, pressing on the median nerve.
This pressure causes pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and wrist — classic symptoms of CTS.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Symptoms usually start gradually and may affect one or both hands. The most common symptoms include:
- Numbness or Tingling
- Often felt in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers.
- May feel like your hand is “falling asleep,” especially at night or when holding a phone or book.
- Pain or Discomfort
- Pain may extend from the wrist up the arm or even down to the fingers.
- Worsens with activity and often disturbs sleep.
- Weakness
- Difficulty gripping objects or performing tasks like buttoning a shirt.
- A tendency to drop things due to hand weakness.
- Burning or Shock-like Sensations
- Sudden jolts of pain may occur in fingers, especially when moving the hand.
- Swollen Feeling
- The fingers may feel swollen even if no swelling is visible.
What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Several factors can contribute to the development of CTS:
- Repetitive Hand Use
- Repeated motions like typing, sewing, or using hand tools over time can irritate the tendons in the wrist.
- Anatomy
- Some people are born with a smaller carpal tunnel, increasing their risk.
- Wrist injuries such as fractures or dislocations can narrow the tunnel.
- Health Conditions
- Diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, rheumatoid arthritis, and obesity can contribute.
- Fluid retention during pregnancy or menopause may increase pressure in the tunnel.
- Gender
- Women are more likely to develop CTS, possibly due to having smaller carpal tunnels.
- Workplace Factors
- Jobs involving repetitive wrist motions or use of vibrating tools may increase the risk.
Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
A healthcare professional will review your symptoms and medical history, followed by a physical examination. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Tinel’s Sign
- Tapping over the median nerve to see if it causes tingling.
- Phalen’s Maneuver
- Bending the wrist to see if symptoms appear.
- Nerve Conduction Studies
- Measures the speed of nerve signals through the carpal tunnel.
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Assesses muscle response and electrical activity in muscles.
- Ultrasound or MRI
- May be used to detect structural problems in the wrist.
Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition. In early stages, non-surgical methods may help relieve symptoms. For more advanced cases, surgery may be necessary.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Wrist Splinting
- Wearing a brace or splint, especially at night, can relieve pressure on the median nerve.
- Activity Modifications
- Changing hand/wrist position during tasks.
- Taking frequent breaks during repetitive activities.
- Medications
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid injections for temporary relief.
- Physical Therapy
- Stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Nerve gliding techniques to reduce pressure.
Surgical Treatment
When symptoms are severe or persist after non-surgical treatment, carpal tunnel release surgery may be recommended. This procedure involves cutting the ligament that is pressing on the median nerve to relieve pressure.
There are two main types:
- Open surgery – a small incision is made in the palm to access the carpal tunnel.
- Endoscopic surgery – a smaller incision with the aid of a camera, resulting in quicker recovery.
Recovery time varies, but most people experience symptom relief and return to normal activities within a few weeks to months.
When to See a Doctor
If you have persistent numbness, tingling, or pain in your hands, it’s essential not to ignore these symptoms. Early intervention can prevent permanent nerve damage and loss of hand function. Consult the Best Orthopedic Doctor in Dhaka to receive expert diagnosis and tailored treatment based on your needs.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
While not all cases can be prevented, certain strategies can reduce your risk:
- Ergonomic Adjustments
- Position your keyboard so your wrists remain straight.
- Use a mouse that allows for a neutral hand position.
- Take Breaks
- Stretch and rest your hands regularly, especially during long typing or manual tasks.
- Proper Posture
- Good posture reduces neck and shoulder tension, which affects nerves in the hands.
- Wrist Exercises
- Simple stretches and exercises can improve flexibility and strength.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
- Manage health conditions like diabetes and arthritis.
- Keep a healthy weight to reduce the risk of nerve compression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome permanent?
A: No, with timely treatment, most people recover fully. However, if untreated, it may lead to permanent nerve damage.
Q2: Can CTS be cured without surgery?
A: Yes, in early stages, CTS can be managed effectively with rest, wrist splints, medications, and therapy.
Q3: How long is recovery after surgery?
A: Recovery usually takes a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the procedure and individual healing speed.
Q4: Is CTS only caused by typing?
A: No, it can be caused by any repetitive wrist motion, health conditions, or anatomical factors.
Q5: Can I still work with CTS?
A: With proper management and ergonomic adjustments, many people continue working during treatment.
Conclusion
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can be a frustrating and painful condition, but early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can make a significant difference. Whether you’re experiencing mild symptoms or severe discomfort, understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and exploring treatment options can help you regain comfort and function. Don’t ignore persistent hand pain — consult the Best Orthopedic Doctor to get expert care and start your journey to recovery